 1 Cypriot pound = 100 cents;aprox. equals to 2.2 U.S dollars.
1 Cypriot pound = 100 cents;aprox. equals to 2.2 U.S dollars.
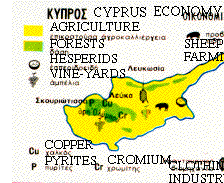 The Cyprian economy is small, diversified, and prosperous.
Industry
contributes 16.5% to GDP and employs 29% of the labor force, while the
service sector contributes 62% to GDP and employs 57% of the labor force.
Rapid growth in exports of agricultural and manufactured products and in
tourism have played important roles in the average 6.8% rise in GDP between
1986 and 1990. This progress was temporarily checked in 1991, because of the
adverse effects of the Gulf War on tourism. Nevertheless in mid-1991, the
World Bank "graduated" Cyprus off its list of developing countries.
The Cyprian economy is small, diversified, and prosperous.
Industry
contributes 16.5% to GDP and employs 29% of the labor force, while the
service sector contributes 62% to GDP and employs 57% of the labor force.
Rapid growth in exports of agricultural and manufactured products and in
tourism have played important roles in the average 6.8% rise in GDP between
1986 and 1990. This progress was temporarily checked in 1991, because of the
adverse effects of the Gulf War on tourism. Nevertheless in mid-1991, the
World Bank "graduated" Cyprus off its list of developing countries.
In the '70s, the economy was basically agricultural, with fruits and vegetables, the chief exports. Farming is highly mechanized, and irrigation is widely used. Although Cyprus has been known since prehistoric times for its minerals - copper(which was named after the island's name-cuprum is the latinic word for copper), iron, pyrites, chrome and asbestos once made up more than a third of all exports - mining is no longer economically important.
After the Turkish invasion of 1974, the growth of the construction industry is observed. Textile manufacturing and other light industries have expanded rapidly in recent times in the free part of the island and world wide recognized as Republic of Cyprus. Cyprus has become also a banking, telecommunications and trade center for international corporations dealing with Middle East. Tourism, a major source of foreign exchange throughout the island, has returned to normal and increases rapidly.
Actual - US$15 million (1993)
 1 Cypriot pound = 100 cents;aprox. equals to 2.2 U.S dollars.
1 Cypriot pound = 100 cents;aprox. equals to 2.2 U.S dollars.
Well noted in the Cyprus Economy are the high educational standard of the
labor force, the labor shortages filled up by foreign workers (5% in 1993
of the gainfully employed), adn Europe absorbs about 57% of exports.

RETURN ![]() TO THE CYPRUS ACCESS PANEL
TO THE CYPRUS ACCESS PANEL