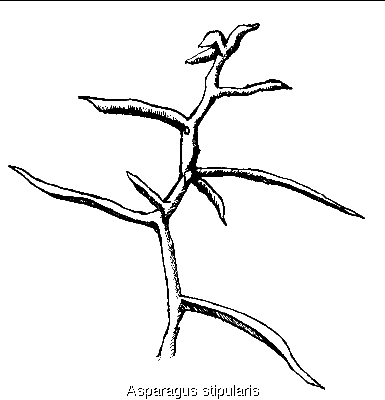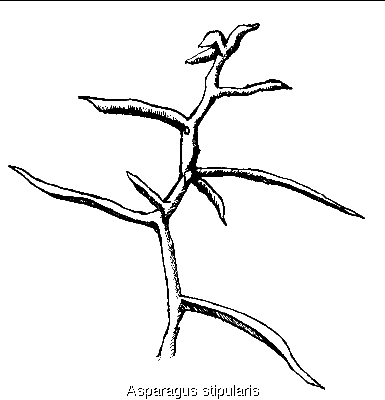ASPARAGUS
(Asparagus stipularis)
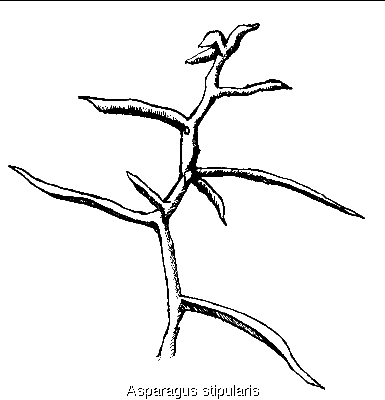
Appearance
A non-aromatic sprawling shrub or climber with smooth,
green stems and leaves reduced to small scales. Branches are stiff and
sharp pointed. Greenish-white, bell-like flowers, in small clusters at
the bases of branchlets, appear between March and June. Fruit a blue-black
berry.
Habitat
Grows on dry rocky or sandy ground by the sea or on rocky slopes
inland or more rarely in thin pine forests, from sea-level to maybe
2,000 ft, but mainly in the lowlands. Widespread.
Uses/Properties
Young shoots of asparagus are collected from the
wild and eaten as vegetables. They are rich in potassium phosphate,
calcium, manganese, cobolt compounds and iron, making them excellent
is cases of anaemia. However, asparagus can cause insomnia if eaten in
large quantities. The plant, especially the young stems, contain asparagine
used as a diuretic in medicine and also in cases of arrhythmia and other
heart complaints. It is also useful for the treatment of bronchitis,
respiratory infections and rheumatism.